Turmeric Extract 95% Curcuminoids
Turmeric is a deep, golden-orange spice known for adding color, flavor and nutrition to foods. It is a relative of ginger, and has been used in cooking for 100s of years.
It has also been used in ayurvedic and other forms of traditional medicine in China and India
Reduces inflammation by blocking enzymes and cytokines that control inflammation, such as COX-2, LOX, and iNOS.
Shown to decrease TNF-a, IL-6, TGF-b, MCP-1, CRP, PGE2, IL-1, IL-8, IL1B and IL-17 as it regulates the TLR4/NF-kB/AP-1 signaling pathway.
Can help restore a normal balance between T cells that cause inflammation (Th 17 cells) and those that protect against it (regulatory T cells).
Curcumin makes up 1-6% of turmeric by weight. There are 3 different forms of curcumin, including curcuminoid, demethoxycurcumin and bisdemethoxycurcumin. Curcuminoid is the only active form and the most potent form.
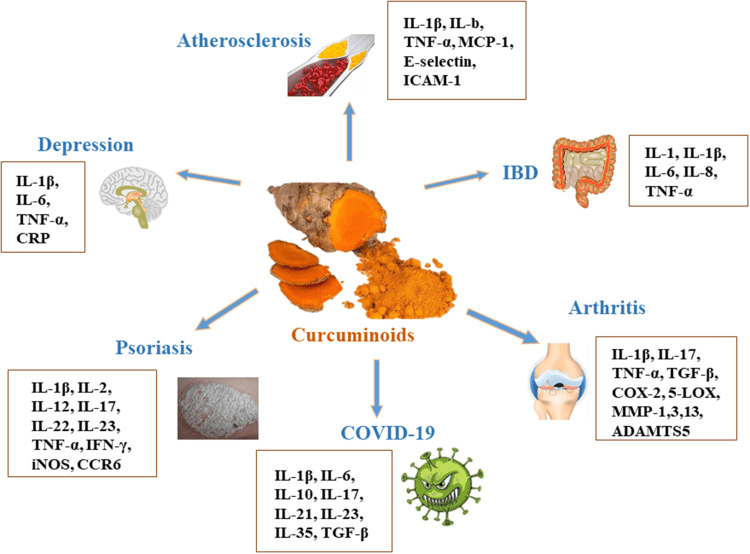

Rich in phytonutrients that may protect the body by neutralizing free radicals (pollution, sunlight) and shielding the cells from damage.
It has powerful anti-inflammatory effects and is a very strong antioxidant.
Attenuating inflammatory response of TNF-a stimulated human endothelial cells by interfering with NF-kB. Also prevents platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)
Scavenging superoxide radicals, hydrogen peroxide & nitric oxide from activated macrophages, reducing iron complex & inhibiting lipid peroxidation.
Curcumin is fat-soluble, but bioavailability is naturally poor, so it is often combined with black pepper (piperine) which enhances absorption by 2,000%.
Can boost brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which plays a role in memory and learning. Disorders like depression and Alzheimer’s have lower levels of BDNF.
Curcumin may be effective in delaying or even reversing many brain diseases and age-related decreases in brain function. It may also help to improve memory and attention.
Improves the function of endothelium, which is the lining of the blood vessels. Endothelial dysfunction is a major driver of heart disease.
Shown it can contribute to the death of cancerous cells, reduce angiogenesis and reduce metastasis.
Curcumin can help clear the buildup of protein tangles called amyloid plaques that cause Alzheimer’s disease.
Is effective for treatment of arthritis, shown to be more effective in relieving pain and is similar to NSAIDS. In RA, it helped reduce disease-related inflammation.
Has shown promise in treating mood disorders, including depression, as it boosts the brain neurotransmitters serotonin and dopamine, reducing inflammation.
Depression has been linked to reduced levels of BDNF and a shrinking hippocampus, and curcumin boosts BDNF levels, potentially reversing some of these changes
Helps with aging, as oxidation and inflammation are believed to play a role in aging, and curcumin addresses these.
Curcumin may promote weight loss and ameliorate obesity-related complications through its antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties.
Shown to significantly reduced BMI, Body Weight and Waist Circumference, especially in patients with diabetes and obesity.
Most dosages commonly exceed 1,000 mg per day. Keep under 12,000 mg per day.
Low side effect profile. Can increase risk of bleeding in people taking Warfarin
Keywords: Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, Improves Endothelium, Prevent Cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, Lupus, Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Depression, IBD, Anti-Aging, Burns belly fat
General Information: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/turmeric-benefits
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/top-10-evidence-based-health-benefits-of-turmeric
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6770259/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7522354/
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/turmeric-vs-curcumin
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7522354/
Anti-Inflammatory: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29097552/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5664031/
Anti-Oxidant: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33172016/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33041781/
Optimizes Brain: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31279955/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1064748117305110?via%3Dihub
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1155/2017/6280925
Endothelium: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28274852/
https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/9/3/746
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8833931/
Anti-Cancer: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6835707/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2212429218303948?via%3Dihub
Alzheimer’s Disease: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5950688/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5796761/
Osteoarthritis: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9605491/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7812094/
Rheumatoid Arthritis: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.338
Depression: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7728608/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6029466/
Anti-Aging: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6429134/
Burns Belly Fat: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36898635/

