Ginger Extract (5% gingerols)
There are over 400 types of compounds present in ginger.
There is enough evidence to prove that ginger possesses multiple biological activities, especially antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacities.
Ginger extract works via the 6-Shogaol for Nrf2 pathwaysP21 and p-P13k.
Ginger inhibits lipid peroxidation through its antioxidant effect. 6-gingerol increases Beclin1 expression to promote autophagy in endothelial cells, and inhibits PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway signaling without affecting cell cycle.
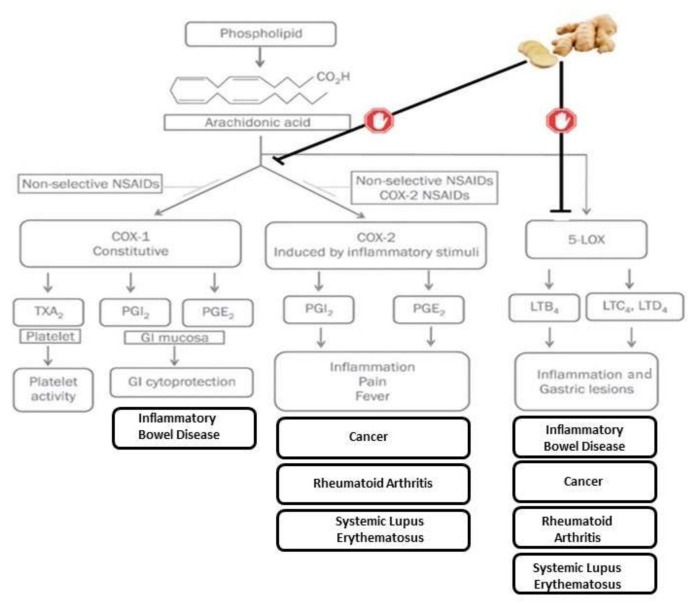
It has analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting COX2 and LOX pathways, therefore preventing arachidonic acid metabolism.
The effect of ginger has been shown to be similar to the NSAIDs family, however, it does not have a negative effect on the stomach mucosa.
Ginger does not act as an inhibitor of COX1, as it is specific to COX2.
Also has anti-microbial, anti-oxidant, anti-allergic activities as well as helping to prevent cancer among numerous other medical conditions.
Stimulates the expression of antioxidant enzymes & reduces the generation of ROS & lipid peroxidation.
Several ginger bioactive compounds such as 6-gingerol, 8-gingerol, 10-gingerol, and 6-shogaol, exhibit antioxidant activity. 6-shogaol = highest activity.
The oxidative stress is mediated by interleukin-1B (IL-1B). Ginger contains a vast amount of antioxidant compounds, nearly 40.

Related to PI3K, protein kinase B & NF-kB. Suppresses pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1, TNFa) and downregulates induction of inflammatory genes.
6-gingerol and 6-shogaol have an anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting the production of inflammatory mediators, such as PGE2, NO, TNF-a, IL-1B and NF-kB.
Antioxidant activity, anti-tumor activity via induction of apoptosis & modulation of genetic activity, Anti-inflammatory and anti-analgesic activity.
They also inhibit COX-1 and COX-2.
6-shogaol decreases NO synthesis more and inhibits arachidonic acid release to a greater extent than 6-gingerol.
Decreases NF-kB in psoriasis, and in lupus 6-gingerol demonstrated a protective attenuating neutrophil extracellular trap release in response to PDE inhibition
Obesity is characterized by elevated levels of pro-inflammatory markers, which benefit from ginger. This process works through the paraoxonase-1 mechanism, avoiding the deposit of lipidic compounds in vessel walls.
Antimicrobial activity, hepatoprotective activity.
Induction of apoptosis via activation of p53. Regulation of inflammatory genes. Reduction of MMP-9 expression.
Suppress hyperproliferation and inflammatory processes leading to carcinogenesis, angiogenesis & metastasis.
Anti-serotoninergic and 5-HT3 receptor antagonistic effects. 6-gingerol inhibits inflammation, tumors, virus, nausea and vomiting.
Normal dose is 250 mg 3-4x/day. Max dose = 4,000 mg/day
Avoid taking ginger if you take blood thinners.
Keywords: Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, Anti-Tumor, Anti-nausea, Autoimmune disease, Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis
Links:
General Information: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK92775/#:~:text=One%20of%20the%20many%20health,and%20potent%20anti%2Dinflammatory%20effects.
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1400956/full
Anti-Inflammatory: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9654013/
Osteoarthritis: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10933899/
https://www.healthline.com/health/ginger-for-arthritis
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10607493/
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/14786419.2016.1236097
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11710709/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26591397/
Pain reliever: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20418184/
Fighting colds: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27574828/

